Elementanalyse: EPMA, EELS
EPMA - Electron Probe Micro Analysis
a) Elektronenstrahlmikroanalyse Ziel der Untersuchungen ist ein verbessertes Verfahren zur quantitativen Elementanalyse mit fundamentalen Parametern, sowie die Bestimmung der Dicke und der Zusammensetzung dünner Schichten. b) tiefenauflösende Elektronenstrahlmikroanalyse Durch neue Entwicklungen auf dem Werkstoffsektor ergibt sich eine wachsende Nachfrage nach zerstörungsfreien, raschen und preiswerten tiefenauflösenden Analyseverfahren. Eine Lösung dieser Aufgabenstellung besteht in einer Quantifizierung von Ionisationswirkungsquerschnitten sowie in der Schaffung eines physikalischen Modells zur Berechnung der Tiefenverteilungsfunktion inhomogener Proben. In diesem Zusammenhang ist auch die genaue Kenntnis der fundamentalen Parameter sowie die Bestimmung der Detektorempfindlichkeit von größter Bedeutung. |
|
Kontakt: R. Svagera, M. Waas |
EELS - Electron Energy Loss Spectrometry
|
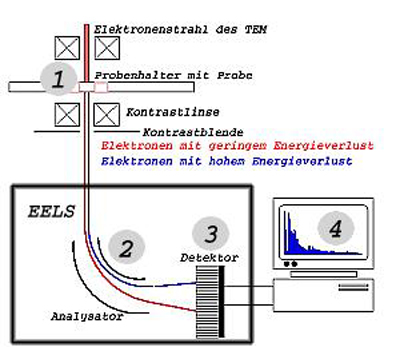
The principle of EELS: the high-energy probe electrons in the TEM lose energy by interaction with the sample. In an energy analyzer the electrons are spatially separated by their different speed, and a spectrum is recorded by means of a CCD. The spectrum contains information about the chemical composition, the optical properties, the density of states (DOS), the magnetic properties, and the bonding of the probed atoms. Chemical analysis down to the nanometer scale is a standard feature of Electron Energy Loss Spectrometry (EELS). The advantages of EELS over other methods are the high spatial resolution of < 1 nm, the low detection limit of a few atoms, and the fact that in contrary to surface sensitive techniques such as AFM, REM, or Auger detection, the electron beam in transmision geometry probes the whole volume. Information available in EELS are (with sub-nm resolution):
|
The principle of EELS
|
Contact: P. Schattschneider, M. Stöger-Pollach |