Rare earth intermetallics
CeNi12B6 |
|
Rare-earth rich 4f-3d system |
|
The family of RT9X4 compounds |
| Cerium based intermetallic compounds are of special interest with respect to their variety of
ground states resulting from the competition between interactions favoring the formation of
symmetry breaking long range magnetic order driven by RKKY-type Ce-Ce intersite
correlations versus interactions such as Kondo screening or frustration effects favoring a
symmetry conserving ground state such as the paramagnetic Kondo lattice state. The
relevance of RKKY-type exchange coupling is generally expected to be lower in systems with
large Ce-Ce interatomic distances. In this context CeNi12B6 is of special interest as it exhibits Ce-Ce interatomic distances as large as 6.07Ǻ.
A very interesting feature of the CeNi12B6 structure displayed in Fig. 1 is the existence of slightly puckered 3342 Ni-nets oriented in the ab-plane. Such d-metal sheets may give rise to highly anisotropic features of the Fermi surface. The remaining nickel atoms are inter- bounded to form pairs of empty [Ni4] tetrahedra coupled by common edges which are highlighted in green colour in Fig.1. We prepared large single crystals via the floating zone method and investigate the ground state properties of the interesting system with possibly highly anisotropic electronic structure and anisotropic magnetic exchange correlations by means of specific heat and magnetisation studies as well as single crystal neutron diffraction. |
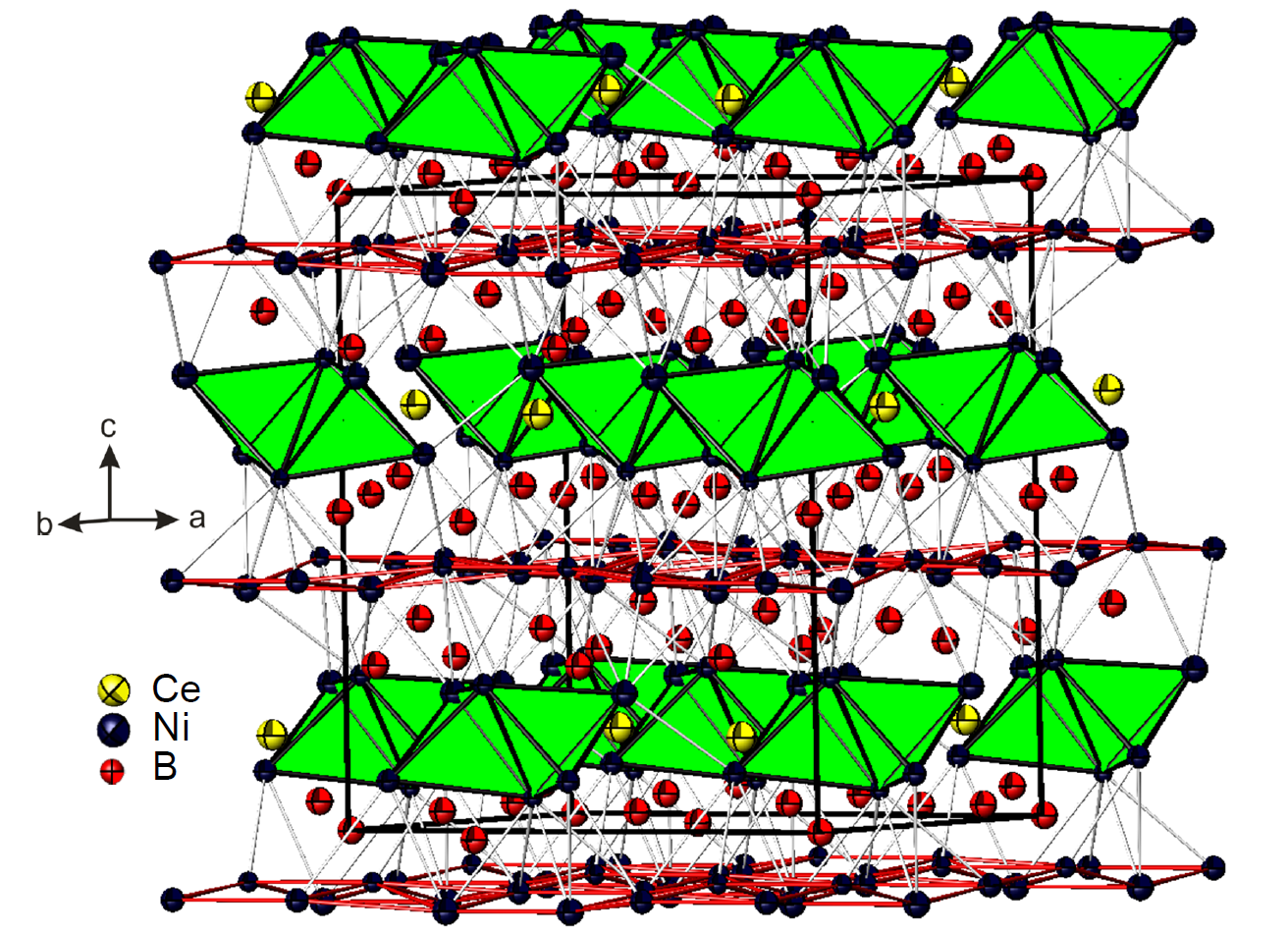
Fig.1: View of the CeNi12B6 structure, space group Cmc21, with emphasis on Ni-Ni bonds. |
Contact: H. Michor, E. Bauer, O. Sologub |
| The R3M family of rare-earth – d-transition-metal compounds with the highest rare-earth content amoung all binary systems.
They crystallize in a low symmetry orthorhombic structure of the Fe3C-type (space group Pnma), which forms only with d-metals having an
almost filled d-band (Co, Ni, Rh). The rare-earth ions occupy two non-equivalent crystallographic positions of 4c and 8d.
The M atoms are located within trigonal prisms formed by the R ions.
An increase of the rare earth content in R-M binary compounds leads to a hybridization of the rare-earth 5d electrons with the unfilled 3d-band that results in the absence of a magnetic moment on the Co and Ni atoms in R3M. The observed narrowing of the 3d-band in R3M in comparison with pure 3d-metals was attributed to reduction in the overlapping of 3d-orbitals owing to the large M-M distance (0.4 nm) in Fe3C-type lattice. Therefore, one may expect a strong correlation between f- and d-electrons and a localisation of spin fluctuations in real space in R3T. Specific heat measurements of some R3M compounds revealed a strong dependence of the T-linear specific heat coefficient γ on the type of R-ion and its concentration. In particular, the γ-value of Y3Co was found to be significantly lower (15 mJ/molK2) than that of isostructural Gd3Co (122 mJ/molK2) and (Gd0.2Y0.8)3Co (350 mJ/molK2). Such a behaviour can be attributed to the presence of a huge contribution of spin fluctuations in the d-electron subsystem induced by the f-d exchange interaction. Moreover, the significant upturn Cp/T for x=0.9 may be associated with the critical behaviour in the vicinity of a quantum phase transition. The above findings motivate further investigations on (GdxY1-x)3M with M = Co, Ni, Rh, .. and other R3M and which have not yet been studied. This project is a cooperation with Prof. N. Baranov at Russian Academy of Science and Ural State University, Ekaterinburg. |
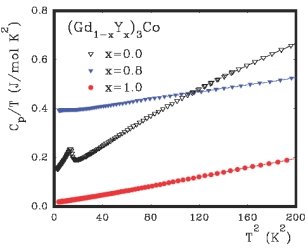
Fig.2: The specific heat of (Gd1-xYx)3Co |
Contact: H. Michor, G. Hilscher |
The family of tetragonal (variant of the cubic NaZn13-type) compounds, RT9X4,
has been very fertile in revealing a wide spectrum of important features including heavy fermion non-Fermi liquid behavior,
model type Kondo lattice behavior, itinerant electron metamagnetism
with indications for metamagnetic quantum criticality and others which are the subject of on-going research.
|
Fig.3: The tetragonal crystal structure (I4/mcm) |
Contact: H. Michor, G. Hilscher |